Quab 188 is available in two grades as aqueous solutions:
- Grade 1: 65% active matter
- Grade 2: 69% active matter
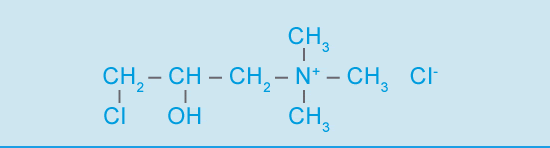
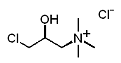
Quab 188 is available in two grades as aqueous solutions:
* Resulting from partial pressure of water in QUAB 188
The product can be stored for prolonged periods (1-2 years) with practically no loss of activity. It is stable at temperatures of up to 50 °C. At higher temperatures, the pH may be slightly reduced over time. However, this does not affect the application properties of the product.
Depending on the total solids content, crystallization may occur at storage temperatures below 0 °C. Total solids are defined as the total of all solid compounds dissolved in the Quab solution.
Crystallization points:
Quab 188 (69 wt.%): below -4 °C (24.8 °F)
Quab 188 (65 wt.%): below -34 °C (-29.2 °F)

Suitable Materials:
Stainless steel types, 316L and 316TI (DIN 1.4571) are basically suitable for transport containers but are recommended for storage only with restrictions. Pickling of containers and pipes with attention to welds is mandatory. These materials are subject to pitting after prolonged periods of contact and at elevated temperatures. However, since transport containers are not subject to prolonged contact, these materials may be used for Quab 188. Plastic containers may be used in all cases.
We recommend a coating for storage tanks made of stainless steel types, 316L and 316TI (DIN 1.4571). Alternatively, fibre reinforced plastic tanks or other coated storage containers may be used. Suitable materials for Quab 188 include polyester, polyethylene, PVC, heat cured phenolic resins or epoxy resins, neoprene, Buna S and Buna N. Enameled containers and tanks may also be used. Any damage in the coating must be repaired.
Unsuitable Materials:
For Quab 188, containers made of boiler plate H II, aluminum (99.5) and stainless steel types, 304L and 321 (DIN 1.4541) are unsuitable. At 50 °C, the corrosion rate of boiler plate H II is 0.2 mm per year, that of aluminum (99.5) 0.1 mm per year. Test samples of stainless steel types, 304L and 321 (DIN1.4541) show pitting of up to 0.05 g/m2 per day.


Additional information (not part of the specifications)
* Epoxide and chlorohydrin together amount to the active content
** Quab-glycol is inert in cationization reactions
*** Undiluted solution
Quab 188 has low acute toxicity and low irritation properties to skin and mucous membranes. It is toxic to the kidneys. A chronic effect through long-term contact cannot be ruled out. Therefore, the product should be handled with appropriate precautions. All contact should be avoided.
Following contact with skin or mucous membranes, flush or clean with plenty of water. Apparatuses and equipment should also be washed with plenty of water. Wash water containing Quad 188 or residual amounts of Quab 188 must be disposed of according to the material safety data sheet.
Conversion with alkali causes the corresponding epoxide (Quab 151) to form. This substantially changes the properties of the solution/mixture. Consequently, the handling instructions for Quab 151 must be observed.